How Instacart Built a Billion-Dollar Grocery Delivery App
From Fridge Frustration to a $10B Empire
In a world where we can stream movies in seconds and hail rides with a tap, why was grocery shopping still stuck in the past?
That’s the question Apoorva Mehta asked himself in 2012—and the answer led to Instacart, now a $10+ billion powerhouse that redefined the grocery industry in the United States.
This is more than a success story—it's a blueprint for how a well-designed grocery delivery app can meet real consumer needs, overcome logistical chaos, and deliver an experience people can’t live without.
Let’s break down exactly how they did it—and how you could too.
Discover how Instacart transformed grocery shopping forever—and how your delivery app idea could be the next big thing with the right tech partner.
Revenue & Valuation: From Zero to Billion-Dollar Beast
Instacart Overview
Launch Year: 2012
Founder: Apoorva Mehta (ex-Amazon Supply Chain engineer)
Head Quarter: San Francisco, California, USA
Employees: 3,000+ (plus 500,000+ gig shoppers across North America)
Industry: On-Demand Grocery Delivery, Retail Tech, Logistics
Market Share: Leading grocery delivery app in the U.S., with ~70% share of app-based grocery delivery
Retail Partnerships: 900+ retailers including Costco, Kroger, Safeway, Publix, ALDI, and more
Global Reach: Operates across the United States and Canada
App Ecosystem: Consumer app, shopper app, retailer portal, and enterprise analytics platform
IPO: Went public in September 2023 with a valuation of ~$10 billion
Revenue (2023): $3.2 billion+
Growth Journey: From Side Hustle to Market Leader
2012
- Apoorva Mehta launches Instacart in San Francisco.
- Drives his own groceries for first customers.
2014-2016
- Raised $275M in Series D from firms like Andreessen Horowitz & Sequoia.
- Expanded to 15 major metro areas.
2020 (Pandemic Pivot)
- Orders skyrocket by 500% in weeks.
- Hired 300,000 new shoppers to meet demand.
- Revenue surged, establishing Instacart as essential infrastructure.
2022–2025
- Shifted from consumer-only to enterprise and health integrations.
- Launched Instacart Health, B2B analytics tools, and warehouse innovations.
- Revenue surged, establishing Instacart as essential infrastructure.
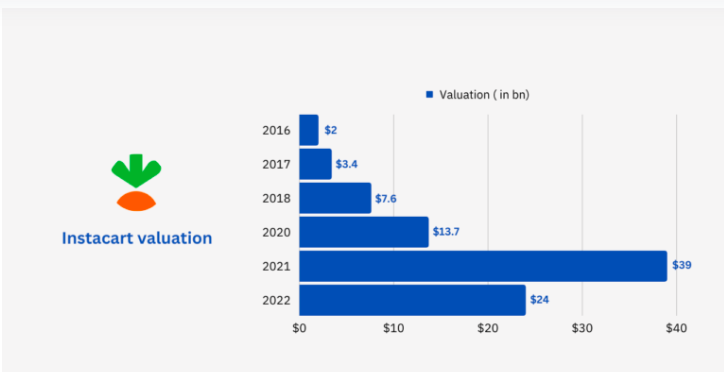
Want your grocery delivery app to scale like this? Let Ventagenie help you architect a future-ready solution.
Instacart users:
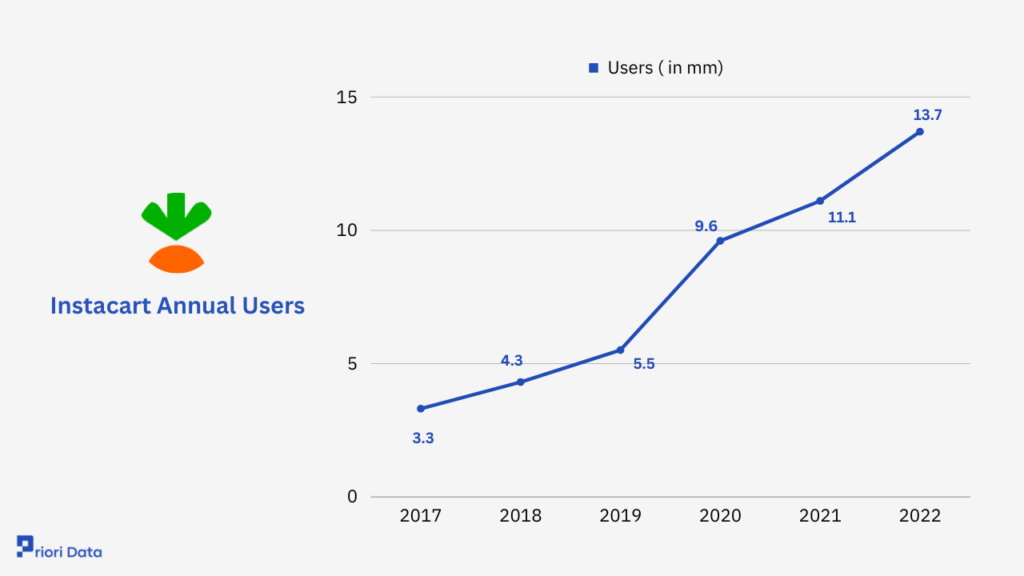
Instacart is used by millions of customers across North America. Users can order groceries and household essentials through the Instacart app and website and have them delivered directly to their door.
How many people use Instacart?
Instacart has an active user base of 13.7 million users in 2022. It shows a 25% increase from the year 2021 i.e. 11.1 million users.
Instacart Annual Users
| Year | Users(in mm) |
|---|---|
| 2017 | 3.3 |
| 2018 | 4.3 |
| 2019 | 5.5 |
| 2020 | 9.6 |
| 2021 | 11.1 |
| 2022 | 13.7 |
Did you know? One of his early startups was a custom cereal subscription service (yes, really). Instacart’s AI can determine optimal substitution items using over 200 factors. Instacart went from side project to $10B IPO in just over a decade—without owning inventory or stores.
Create Clone App Like Instacart
What Made Instacart’s Grocery App Work ?
Asset-Light Logistics
-
No need for stores, trucks, or warehouses.
-
Tapped into existing retail infrastructure—scalable & cost-effective.
Just-in-Time Labor
-
Leveraged gig economy for peak demand.
-
Shoppers earn per delivery, providing hyperlocal delivery.
AI and Smart Tech
-
Custom recommendations, smart reorders, and instant coupon applications.
-
Route optimization, real-time item substitution, and demand prediction.
Strategic Partnerships
-
Deals with Costco, Walmart, Kroger, and local stores gave access to millions of SKUs without owning inventory.
Personal Touch
-
Shoppers chat with customers, offer substitutions, and customize orders—mixing automation with humanity.
The Problem Instacart Solved
Grocery shopping was ripe for disruption. The pain points were clear:
- Wasted time driving to and from stores
- Long checkout lines and parking hassles
- Limited time for families and working professionals
- Health concerns during the pandemic
- Inaccessible options for seniors, disabled, or homebound individuals
People didn’t just want groceries—they wanted convenience, speed, safety, and control.
How Instacart Solved It
Instacart didn’t open stores or warehouses. Instead, it built a tech layer on top of existing grocery infrastructure and empowered everyday people to shop for others.
That decision turned out to be genius. Here's how the model worked:
1. Smart Use of Existing Stores
- Partnered with major retailers like Costco, ALDI, Safeway, Publix, Wegmans
- Avoided inventory costs, leasing, and storage issues
2. Gig-Powered Fulfillment
- Employed contracted shoppers to hand-pick and deliver items
- Could scale quickly without building warehouses or owning trucks
3. Real-Time App Experience
- Customers could track deliveries live, chat with their shopper, and approve substitutions on the fly
4. Seamless Checkout & Payments
- Multiple payment methods, digital coupons, and discounts built in
Features of Instacart which like by Users
Instacart wasn’t just functional—it was intuitive, thoughtful, and personalized. These are the features that made it a favorite:
- Order from multiple stores in one app
- AI-powered smart substitutions when items are out of stock
- Apply manufacturer coupons automatically
- “Buy it again” recommendations based on past behavior
- Real-time GPS tracking for deliveries
- Direct chat with your shopper during the process
- Schedule deliveries in advance, even up to a week out
- Health and dietary filters (vegan, keto, gluten-free, organic)
Challenges Instacart Faced (and Beat)
No success story comes without struggle. Instacart’s journey was full of them—and each one offers a lesson for anyone entering the grocery delivery space.
Labor Tensions
- Shoppers protested over low wages, tip policies, and lack of benefits.
- Solution: Transparent tipping, improved shopper support tools, and better pay structures.
Profitability Problems
- Logistics are expensive. For years, the company operated at a loss.
- Solution: Added ads, subscriptions (Instacart+), enterprise tools, and B2B offerings to diversify revenue.
Fierce Competition
- Entered a market later dominated by Amazon Fresh, DoorDash, and Walmart.
- Solution: Invested in AI, built superior user experience, and became retailers' ally instead of a threat.
Post-COVID Drop-Off
- After explosive pandemic growth, user activity started to slow.
- Solution: Shifted toward healthcare delivery, analytics, and long-term retention features.
Building a grocery delivery app? These features are no longer optional—they’re expected.
Instacart’s Future (And Yours)
As Instacart expands into healthcare, predictive nutrition, and B2B retail tech, the space for next-gen grocery delivery apps is wide open.
Whether you're targeting:
- Sustainable local produce delivery
- Fitness-focused meal kits
- Doctor-prescribed grocery baskets
- Hyperlocal convenience delivery
Ventagenie has the tools and team to bring your delivery app vision to life.
Ready to Launch Your Own Instacart Like Grocery Delivery App ?
Frequently Asked Questions
Instacart is a U.S.-based on-demand grocery delivery and pickup service. Users can order groceries through the app or website from local stores like Costco, Safeway, and ALDI. A personal shopper picks and delivers the items—often within hours.
No. Instacart operates as a tech platform, partnering with existing grocery retailers. It doesn’t own inventory or warehouses, which allows for fast scalability and low overhead.
Instacart uses a network of independent contractors known as shoppers. Some shop and deliver, while others only shop. This gig-based model allows Instacart to scale flexibly across different regions.
Instacart earns revenue through:
- Delivery fees and service charges
- Instacart+ subscriptions (free delivery perks)
- Retail partnerships and promotions
- Advertising from consumer brands
- Enterprise data tools for retailers
-
Order from multiple stores
-
Real-time tracking and shopper chat
-
Smart AI-driven substitutions
-
Integrated coupons and loyalty cards
-
Advance scheduling and recurring orders
-
Dietary filters (organic, vegan, gluten-free, etc.)
Instacart has historically struggled with profitability due to logistics costs, but it has improved its financials by diversifying revenue streams—especially through ads and B2B tools for retailers. It went public in 2023 with a $10B+ valuation.
-
Labor disputes with gig workers
- Competition from Amazon, Walmart, and DoorDash
- High operational costs
- Post-pandemic user drop-off
- Maintaining long-term customer loyalty
Absolutely! The market still has room—especially in:
-
Local and regional delivery services
-
Niche markets (organic, ethnic, meal kits, etc.)
-
Healthcare-focused grocery solutions
-
B2B grocery logistics for small retailers
Instacart’s pricing varies depending on your order and preferences. Here’s a breakdown of potential fees you might encounter:
-
Delivery Fee: Starts at $3.99 for same-day orders over $35. Fees may increase for orders under $35 or for 1-hour expedited deliveries.
-
Heavy Order Fee: An additional charge applies to orders exceeding 50 pounds in total weight. While the exact amount isn’t specified, it helps cover the effort of transporting heavier items.
-
Service Fee: This fee supports platform operations and varies based on your location and whether your order includes alcohol.
-
Long-Distance Service Fee: If you're ordering from a store located 30 to 60 miles away, an extra charge may apply to cover the extended delivery range.
-
Priority Delivery Fee Want it fast? Priority delivery starts at $2, ensuring your order arrives within 60 minutes.



